NEUROMARKETING AS A PARADIGM OF MARKETING AND A TOOL FOR INFLUENCING CONSUMERS
Журнал: Научный журнал «Студенческий форум» выпуск №20(329)
Рубрика: Экономика

Научный журнал «Студенческий форум» выпуск №20(329)
NEUROMARKETING AS A PARADIGM OF MARKETING AND A TOOL FOR INFLUENCING CONSUMERS
Abstract. The relevance of the research topic lies in the fact that the results obtained from psychophysiological studies assert that not only the traditionally considered factors influence a consumer's purchasing decision, but also color, images, smell, sound, and letter combinations – all these factors determine the customer's choice in favor of a particular product. Thus, the effectiveness of modern marketing technologies increasingly depends on creative solutions, and researchers often encounter situations where well-established approaches to various types of marketing activities are becoming exhausted.
Keywords: neuromarketing, marketing, management, economics, psychology, neuropsychology
Chapter 1. Neuromarketing as a Modern Tool for Ensuring Sustainable Company Functioning in the Contemporary Market
1.1. The Essence and Socio-Economic Significance of Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing is the use of neurophysiological tools, such as eye-tracking, skin conductance measurement, EEG, and MRI, to achieve marketing goals. By analyzing bodily reactions and brain functioning, neuromarketers have been able to create a database capable of deciphering the mysteries of consumer choice.
Currently, six key areas of application are identified in neuromarketing:
1. Brands. The substantive foundation of brands lies in their ideological content, which is embedded in the minds of consumers. In modern realities, neuromarketing implements effective methods to create associations related to brands in order to thoroughly understand their perception.
2. Product Design. Neuromarketing evaluates consumer reactions to specific product design ideas and packaging. These consumer reactions are typically automatic and highly emotional, characterized by their unconscious nature.
3. Advertising. It is important to note the tremendous effectiveness of the proposed advertising, which primarily influences at the subconscious level, despite the fact that consumer persuasion may be contrary. Neuromarketing studies the mechanisms of advertising's impact on consumers and develops methods for its optimization.
4. Consumer Decision-Making in Product Purchases. Neuromarketing demonstrates how the shopping environment influences the decision-making process of consumers.
5. Online Shopping. The digital world has presented new challenges to our outdated brains. Scientific research in the field of neurobiology reveals numerous ways to influence people's behavior in the online environment.
6. Effectiveness of Entertainment. Entertainment creates a unique experience in people's minds, which can significantly influence their preferences and actions. As a result, neuromarketing helps to understand how entertainment shapes attitudes.
1. 2. Neuromarketing as an Interdisciplinary Science
Moreover, neuromarketing is a discipline at the intersection of classical marketing and neurology, which studies the functioning of the human brain:
1. Studying consumer reactions to stimulus.
2. Forecasting consumer demand and criteria for choice.
3. Stimulating purchases at the unconscious level.
Chapter 2. Analysis of the Practice of Applying Neuromarketing as a Paradigm of Marketing and Tools for Influencing Consumers
2.1. Neuromarketing Trends Worldwide
Many leading brands actively utilize neuromarketing laboratories to test their hypotheses. For example, Coca-Cola employs neuroimaging technologies for preliminary analysis of the effectiveness of its advertising campaigns. As a result, the brand's video ads, banners, and other marketing materials demonstrate high success rates.
Victoria’s Secret uses two obvious neuromarketing tactics to position itself as an exclusive women's lingerie brand. Firstly, the color pink is associated with femininity, charm, and romance. Secondly, the very word "secret" encourages customers to show greater interest and delve into the meaning behind the brand name.
KFC employs several psychological triggers to stimulate various senses. The company uses phrases like "finger-lickin' good," appealing to taste buds, emphasizes the color red to prompt action, and incorporates short, catchy advertising jingles in its restaurant halls to capture attention and remain memorable to visitors.
PayPal is one of the few brands that has completely transformed its value proposition strategy through neuromarketing. Analyzing its advertising content reveals that the brand now promotes itself as a fast and secure solution for limitless payments. Previously, PayPal marketed itself as a safe payment solution, but after consulting neuroscience, it optimized its marketing campaign. Once the company discovered that people preferred speed over security, it changed its brand message.
Nike is a master of neuromarketing.
The sports brand often engages influential personalities and uses inspiring scenarios in its advertising to evoke specific types of reactions. For instance, during the 2018 World Cup in Russia, Nike hired a technology company equipped with artificial intelligence software to conduct competitive analysis.
When the results came in, it turned out that people preferred the advertisement featuring the famous footballer Cristiano Ronaldo.
Supermarket Walmart and IKEA also utilize neuromarketing strategies effectively.
2.2. Characteristics of Neurocognitive Aspects of Consumer Behavior
Let us consider examples of how neuromarketing techniques influence consumer behavior.
One such method is the proper focus of customer attention. For instance, in the first example of outdoor advertising, the main focus was on the child's face. In the second image, however, the child's face is oriented towards the textual advertisement, which helps reinforce the conveyed message.
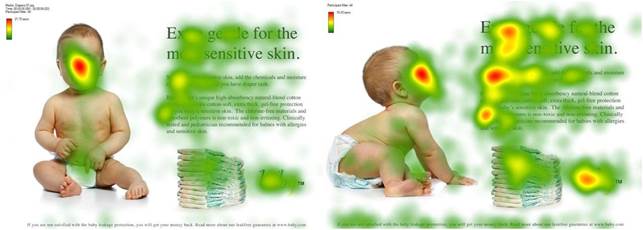
Figure 1. Example of advertising
The use of visual effects is a practical neuromarketing tool. Marketers utilize various colors, prints, fonts, styles, and contours in their advertising efforts. The use of different colors elicits distinct reactions; for example:
- Red stimulates the brain. When combined with black and gold, it creates a romantic atmosphere, a sense of freedom, and purity.
- Yellow attracts consumer attention and is retained in memory for a longer period. Marketers often use yellow in advertising for premium car brands.
- Blue fosters feelings of confidence, reliability, and protection in the mind. For example, advertising for Orbit chewing gum, designed in blue, creates a sense of trust.
- Brown is suitable for conservative and practical audiences. It provides comfort and reassurance.
Each color has numerous shades, and each can stimulate the brain to evoke different emotions. For example, milk packaging is often designed in a light brown (milk color) to give the impression of freshness directly from the farm, appealing to the target audience.
Smell influence is another powerful neuromarketing tool. Marketers attract consumers' attention with specially developed scents for premium brands such as Mercedes, Audi, Porsche, and Rolls-Royce. These fragrances can be experienced both in showrooms and inside vehicles. They highlight the qualities the brand aims to showcase—dynamism, exclusivity, and luxury.
Taste influence is also a key neuromarketing approach. Flavor experiences, such as free tastings, are among the most common methods of impacting consumers. During a tasting, customers can try the product directly in the store and assess its flavor. Companies that regularly conduct tastings gain an advantage over competitors because, after experiencing the product, the likelihood of purchase increases significantly.
Chapter 3. Global and Russian Experience in the Successful Application of Neuromarketing by Companies
Neuromarketing encompasses a wide range of methods and approaches that significantly simplify interactions between consumers and producers. These tools help sellers to market their products under favorable conditions.
For example, in the development of advertising for the CarBakers Skoda Fabia model, eye-tracking technology was used. Researchers focused on increasing brand awareness for Skoda by emphasizing the company’s logo rather than the model name, as had been done previously.
The company Oticon, known for manufacturing children's hearing aids, conducted a neuromarketing study aimed at overcoming negative perceptions associated with aging and frailty. As a result of the research, a new trendy design for hearing aids was developed, which helped improve the product’s image in the eyes of consumers.
The global automotive giant Volkswagen also employed eye-tracking methods and visual structuring in its advertising campaigns. A video released by the company gained widespread popularity due to its closing phrase, "Safety exists!", which was emphasized to enhance brand recognition.
Neuromarketing in cinema. In the film industry, neuromarketing helps explore viewers’ reactions to plot development, special effects, and different possible endings. For instance, studies were conducted on the film "The Good, the Bad and the Ugly," revealing that the movie tends to evoke quite stereotypical reactions among viewers. Some producers engage neuromarketing specialists to analyze research results and select the most appealing ending for audiences.
Innerscope Research organized an interesting neuromarketing study: a group of 1,000 viewers watched trailers of 40 movies. During the screenings, biometric indicators such as heart rate, sweating, breathing activity, and eye reactions were measured. The findings showed that action-packed adventure films evoke the strongest responses. Perhaps this is why "Pirates of the Caribbean: At World’s End" managed to gross $90 million in just the first few days of release. From this, we can conclude that applying neuromarketing in filmmaking can help predict a film’s success or failure in advance.
Russian cinema has also followed the example of its international counterparts by utilizing neuromarketing technologies. The project "Neurotrend" tested films such as "Yolki 1914," both parts of "Gorko," "Legend № 17," and "Ekipazh" to identify consumer needs early on and to predict the potential success of these movies.
Conclusion
In summary, neuromarketing is a vital tool in modern marketing, ensuring the sustainable functioning of a company within a competitive market environment. As an interdisciplinary science, neuromarketing combines knowledge from various fields, enabling more precise and detailed research into consumer behavior. This, in turn, facilitates the development of more effective strategies for promoting products and services in the marketplace.
The successful experiences of both global and Russian companies in applying neuromarketing confirm its effectiveness in increasing sales and enhancing interactions with consumers. Companies that integrate neuromarketing methods into their operations gain a competitive edge and achieve greater success in the market.
Therefore, neuromarketing is not only a contemporary paradigm in marketing but also exerts a significant influence on consumers, making it an integral part of a company's successful marketing strategy in today’s dynamic market conditions.

