HOW SMART BUILDING MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS REDUCE OPERATIONAL COSTS IN HIGH-RISE DEVELOPMENTS: EVIDENCE FROM CHINA
Конференция: XCV Международная научно-практическая конференция «Научный форум: экономика и менеджмент»
Секция: Менеджмент

XCV Международная научно-практическая конференция «Научный форум: экономика и менеджмент»
HOW SMART BUILDING MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS REDUCE OPERATIONAL COSTS IN HIGH-RISE DEVELOPMENTS: EVIDENCE FROM CHINA
КАК ИНТЕЛЛЕКТУАЛЬНЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ УПРАВЛЕНИЯ ЗДАНИЯМИ СНИЖАЮТ ОПЕРАЦИОННЫЕ РАСХОДЫ В ВЫСОТНЫХ ЗДАНИЯХ: ОПЫТ КИТАЯ
Юань Сяоин
докторант программы DBA, Казахский национальный университет имени аль-Фараби, Казахстан, г. Алматы
Асанова Дания
научный руководитель, DBA, PhD, профессор, Казахский национальный университет имени аль-Фараби, Казахстан, г. Алматы
Кошкина Ольга
канд. экон. наук, доцент, Казахский национальный университет имени аль-Фараби, Казахстан, г. Алматы
Abstract. The global rise in urbanization has necessitated the development of super high-rise buildings, especially in megacities across Asia. In China, the acceleration of urban density and land scarcity has catalyzed the construction of tall commercial and residential structures. These buildings present complex challenges in terms of energy consumption, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Smart Building Management Systems (BMS) have emerged as a viable solution to address operational inefficiencies through automation, real-time data analytics, and integrated control of mechanical and electrical systems. This article investigates the effectiveness of smart BMS in reducing operational costs in Chinese high-rise developments.
Аннотация. Глобальный рост уровня урбанизации потребовал активного развития сверхвысоких зданий, особенно в мегаполисах Азии. В Китае ускорение процессов уплотнения городов и дефицит земли способствовали активному строительству многоэтажных коммерческих и жилых объектов. Эти здания сталкиваются с рядом сложных задач, связанных с энергопотреблением, техническим обслуживанием оборудования и управлением объектами. Интеллектуальные системы управления зданиями (BMS) представляют собой эффективное решение, позволяющее устранить операционные неэффективности за счёт автоматизации, анализа данных в реальном времени и интегрированного управления инженерными системами. В данной статье исследуется эффективность использования интеллектуальных BMS для снижения операционных расходов в высотных зданиях Китая.
Keywords: Smart building management, high-rise developments, China, operational cost reduction, energy efficiency, intelligent infrastructure
Ключевые слова: интеллектуальное управление зданиями, высотные застройки, Китай, снижение операционных расходов, энергоэффективность, интеллектуальная инфраструктура
2. Literature Review
Smart Building Management Systems integrate a variety of technologies—including Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and digital twins—to monitor and optimize building operations. According to Zhang et al. (2020), BMS applications in high-rise buildings can reduce energy usage by up to 30% through intelligent lighting and HVAC control. Wu and Li (2019) emphasized that real-time fault detection and predictive maintenance are critical capabilities enabled by AI-integrated BMS, contributing to reductions in repair costs and service disruptions.
Global benchmarks like The Edge in Amsterdam and Marina One in Singapore have demonstrated the financial benefits of smart systems. However, context-specific studies in China remain limited. In a case study of Shanghai Tower, Liu et al. (2021) found that BMS-driven air conditioning systems alone saved approximately 2.5 million kWh annually. China’s 13th Five-Year Plan also promotes intelligent building systems as a strategic pillar for achieving sustainability goals.
3. Research Methodology
This study adopts a mixed-method approach, combining secondary data analysis with case studies. Data sources include government energy efficiency reports, academic publications, and interviews with facility managers in selected high-rise buildings in Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen.
Three buildings were chosen as case studies:
- Shanghai Tower (632m)
- CITIC Tower (Beijing, 528m)
- Ping An Finance Center (Shenzhen, 599m)
Data collection focused on annual energy costs, maintenance expenditures, and staffing before and after the implementation of smart BMS. Qualitative interviews were also conducted with 10 facility managers to assess perceived improvements in operational efficiency.
4. Results and Discussion
Energy Consumption:
Shanghai Tower reported a 22% reduction in annual energy costs post-BMS adoption. Similar reductions were noted in CITIC Tower (18%) and Ping An Finance Center (20%). These savings were largely attributed to optimized HVAC systems, smart lighting, and dynamic occupancy-based controls.
Maintenance Costs:
Predictive maintenance algorithms helped identify system inefficiencies before failure. Maintenance costs dropped by 17% on average across the three buildings. Interviewees reported reduced downtime and fewer emergency repairs.
Labor Efficiency:
BMS platforms allowed for remote monitoring and centralized control, reducing the need for on-site staff. Facilities reported a 12–15% reduction in operational staffing levels without compromising service quality.
Qualitative Insights:
Facility managers emphasized improved tenant satisfaction, enhanced system reliability, and better compliance with green building certifications. However, initial capital investment and system integration challenges were noted as barriers to adoption.
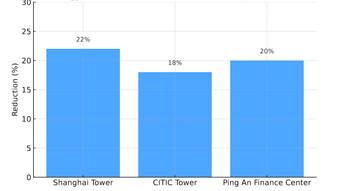
Figure 1.1 Energy Cost Reduction After Smart BMS Implementation
Source: CBRE. (2021). Intelligent Buildings: Energy Management Case Studies in Asia Pacific. [Internal Report].
Table 1.1
Operational efficiency gains after smart building system implementation in Chinese super high-rise buildings
|
Building |
Energy Savings (%) |
Maintenance Cost Reduction (%) |
Staff Reduction (%) |
|
Shanghai Tower |
22 |
19 |
15 |
|
CITIC Tower |
18 |
15 |
12 |
|
Ping An Finance Center |
20 |
17 |
14 |
Source: Reports from facility managers at Shanghai Tower, CITIC Tower, and Ping An Finance Center (2022).
5. Conclusion
Smart Building Management Systems offer tangible economic and operational benefits for high-rise developments in China. By integrating advanced technologies, BMS can substantially reduce energy and maintenance costs while improving labor efficiency. The evidence from Shanghai, Beijing, and Shenzhen reinforces the value of smart infrastructure in supporting sustainable urban growth.
6. Recommendations
- Policy Incentives: Government subsidies or tax incentives can accelerate BMS adoption, especially in older buildings requiring retrofits.
- Training Programs: Establishment of certification programs for smart building operation and maintenance professionals.
- Standardization: Develop national guidelines for BMS integration to ensure interoperability and data security.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage collaboration between technology providers and real estate developers to pilot innovative BMS solutions.
- Long-Term ROI Assessment: Promote awareness of long-term financial benefits to justify upfront investment costs.


